The Renaissance
The Renaissance, spanning from the 14th to the 17th century, was a transformative cultural, intellectual,
and
artistic
movement in Europe. Emerging from the Middle Ages, it marked a revival of interest in classical
learning,
literature,
and art. Characterized by a humanistic approach that emphasized individualism, reason, and a renewed
focus
on
the
potential of human achievement, the Renaissance saw a resurgence of classical texts, the development of
new
artistic
techniques, and scientific advancements. Notable figures like Leonardo da Vinci, Michelangelo, and
Raphael
excelled in
various artistic fields, while thinkers such as Petrarch and Erasmus contributed to the revival of
classical
ideas. The
period had a profound impact on literature, philosophy, science, and art, laying the groundwork for the
profound
cultural shifts that would follow.
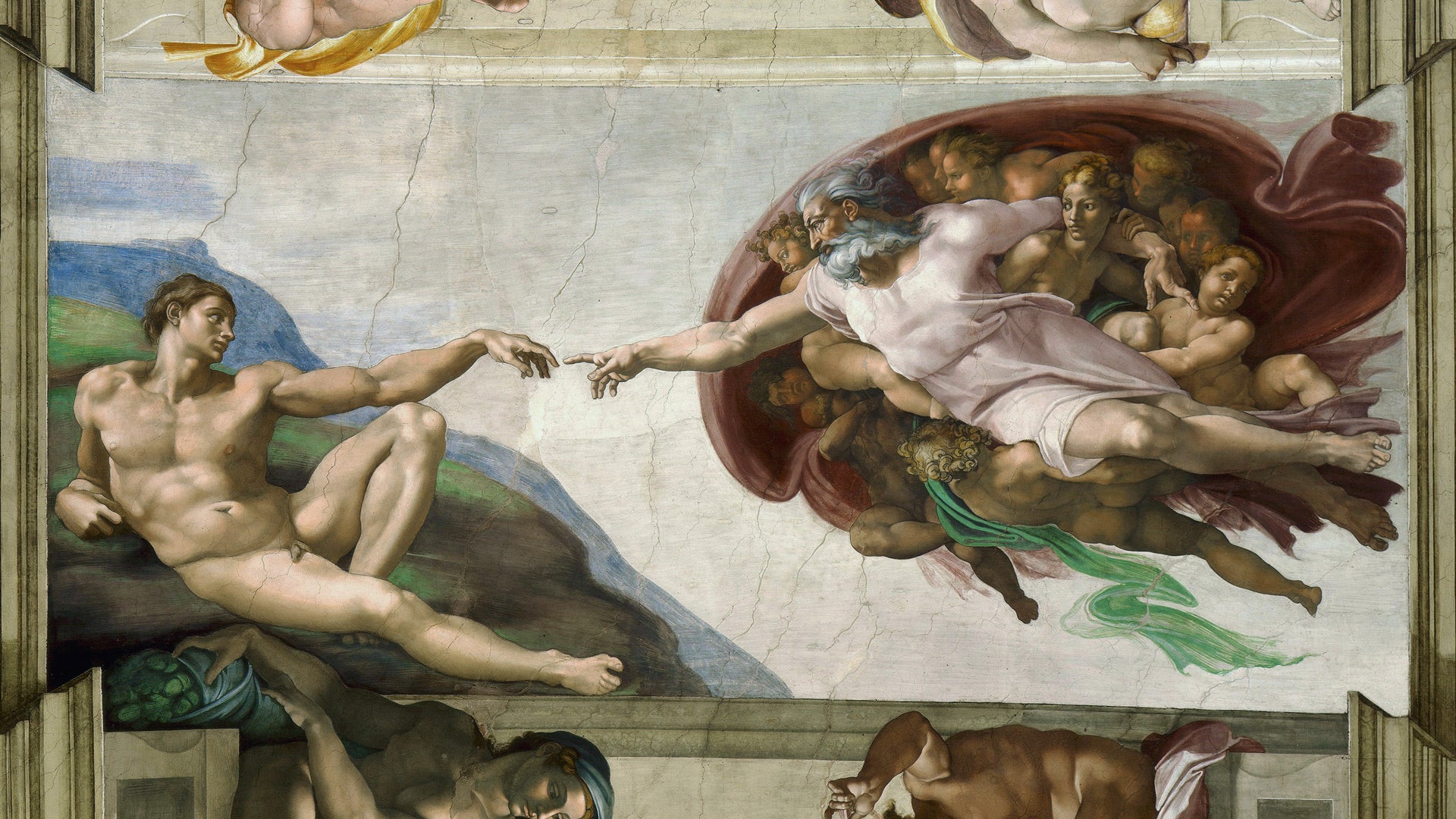

The King of The Renaissance
Leonardo da Vinci (1452–1519) was a polymath of the Italian Renaissance, renowned for his mastery in
diverse fields.
Born in Vinci, he apprenticed under Andrea del Verrocchio in Florence, where his artistic talents
flourished. Leonardo's
insatiable curiosity led him to excel not only in painting but also in anatomy, engineering, and natural
sciences. His
notebooks reveal groundbreaking observations on anatomy and detailed sketches of inventions centuries
ahead of his time.
Iconic works like "The Last Supper" and "Mona Lisa" showcase his innovative techniques, including
sfumato. Operating at
the intersection of art and science, da Vinci's contributions extended to optics, engineering designs,
and
conceptualization of flying machines. His legacy endures as a symbol of intellectual brilliance,
curiosity, and artistic
innovation, influencing generations to come.

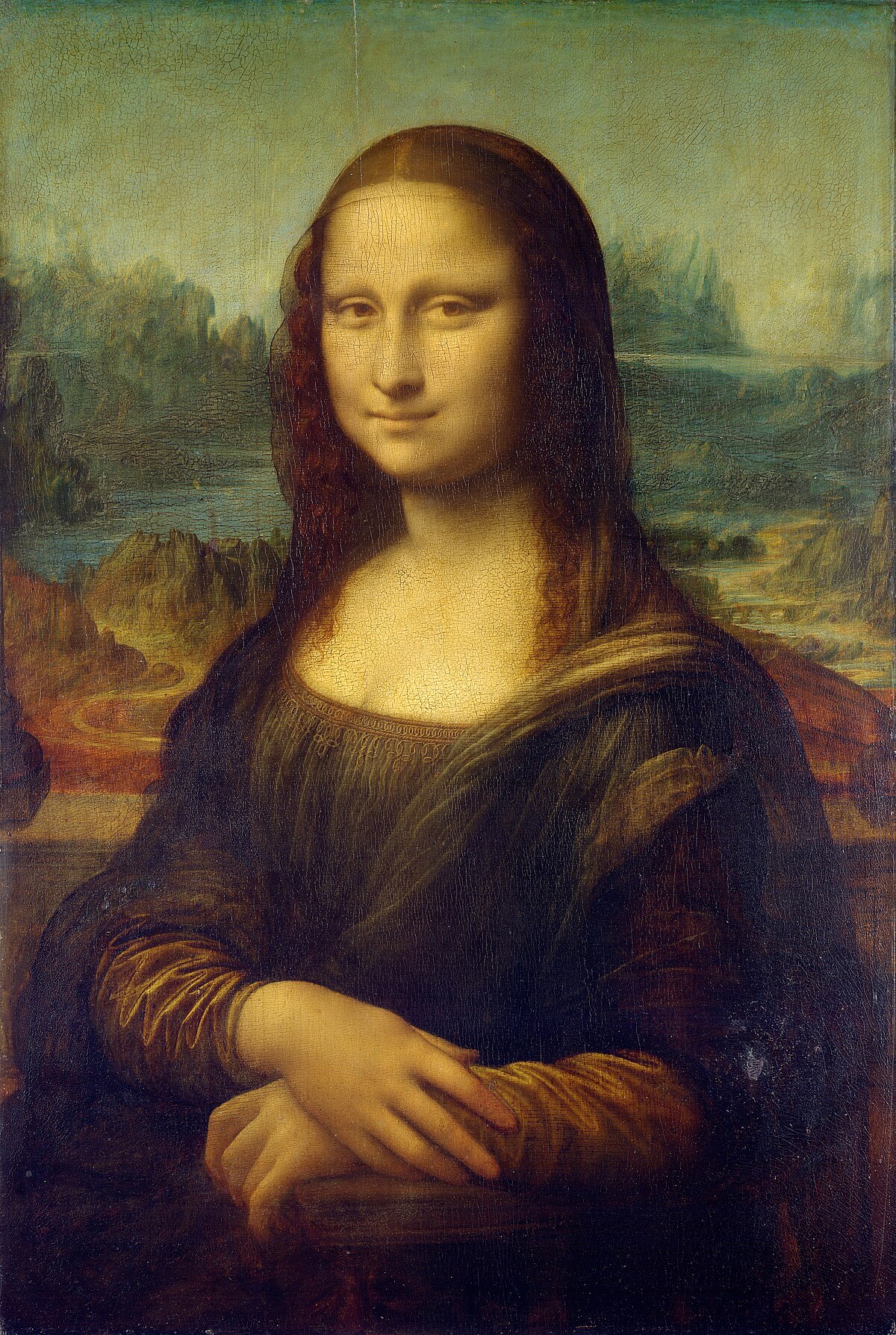
Mona Lisa
Painted between 1503 and 1506, the "Mona Lisa" is Leonardo's renowned portrait of Lisa Gherardini, known
for her elusive
smile and the masterful use of sfumato, creating a lifelike, mysterious atmosphere.

The Last Supper
Executed from 1495 to 1498, this monumental mural in Milan's Santa Maria delle Grazie depicts the
dramatic moment when
Jesus announces betrayal. Leonardo's meticulous details and perspective capture the emotional intensity
of the scene.

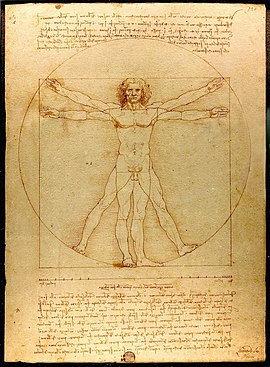
Vitruvian Man
Created around 1490, this iconic drawing illustrates the proportions of the human body within both a
square and a
circle. Inspired by the architect Vitruvius, it symbolizes Leonardo's fusion of art and scientific
exploration.